 Getting Started[an error occurred while processing this directive]:
Preparations
Getting Started[an error occurred while processing this directive]:
Preparations
| Think Differently. Think MkLinux. | |
 Getting Started[an error occurred while processing this directive]:
Preparations
Getting Started[an error occurred while processing this directive]:
Preparations
|
| ||||
| Home | About | News | FAQ | Getting Started | Using MkLinux | Advanced Admin | |||||
[an error occurred while processing this directive]
 Previous Previous
|
[an error occurred while processing this directive]

|
[an error occurred while processing this directive]
Next
|
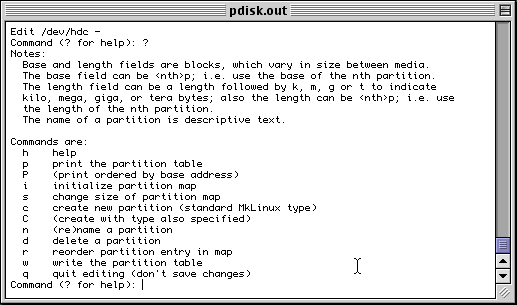
The main problem is that pdisk is not a typical Mac OS application. It has a command-line interface that can be intimidating to many. Another disadvantage is that it does not do anything to areas of the disk other than the partition map. Consequently it cannot install a driver onto your disk, nor can it create HFS or HFS+ volumes. (However, it is important to note that it is not necessary to have a driver partition on a disk that doesn't have an HFS partition.)
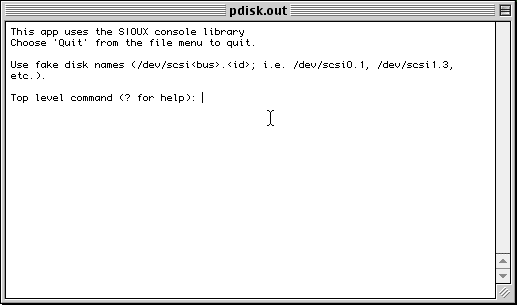
Pdisk has two variants. One is a program that runs under Mac OS. The other is a MkLinux program that is available to you when the MkLinux installer is running. The Mac OS version uses Mac OS facilities to access the disks; the MkLinux version uses MkLinux's facilities. However, the "engine" in pdisk is the same between the two versions. So, once you learn to use one, you will know how to use the other.
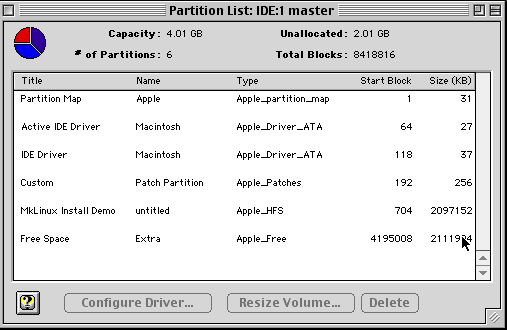
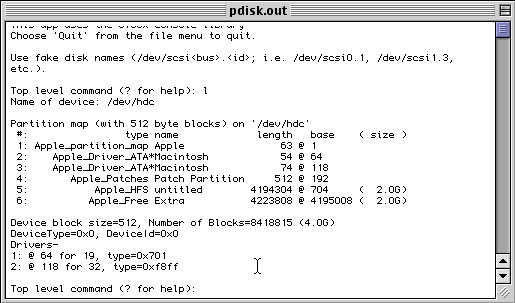
Even though it can be intimidating at first, we recommend that you learn enough of pdisk to at least display the partition table on a disk. A good reference on how to use pdisk can be found here. Of all the partitioners mentioned, pdisk is the best one to show your disk's true partition layout.
Partitioning using pdisk(MacOS)
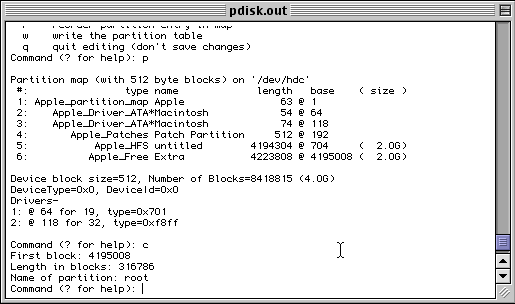
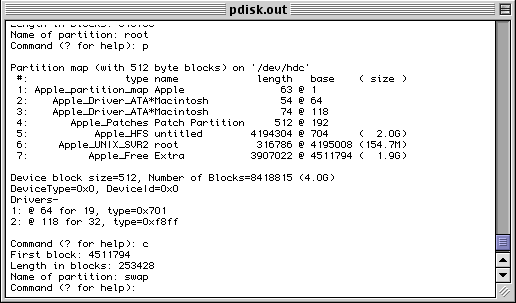
[an error occurred while processing this directive]
 Previous Previous
|
[an error occurred while processing this directive]

|
[an error occurred while processing this directive]
Next
|
| Home | About | News | FAQ | Getting Started | Using MkLinux | Advanced Admin |
Contact the web team at [email protected].
Copyright (©) 2001 MkLinux Developers Association. Permission to freely distribute this document is hereby granted, provided that it is distributed at no charge other than normal connect-time charges. All rights other than those specifically granted above are reserved.